Space
We may finally find ALIENS by 2026, thanks to NASA’s new space telescope

(Planet Today) The National Aeronautics and Space Administration‘s (NASA) James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) may be able to provide evidence of aliens as early as 2026. This is according to Caprice Phillips of the Ohio State University, who found with her colleagues that Webb can detect signs of alien life in three days or so. Phillips said that after a few orbits, the telescope will have collected enough data to tell whether aliens exist.
(Article by Virgilio Marin republished from NaturalNews.com)
“What really surprised me about the results is that we may realistically find signs of life on other planets in the next five to 10 years,” Phillips remarked. She presented their findings during the American Physical Society April Meeting.
NASA telescope facilitates search for alien life
When searching for alien life, some of the most promising planets to explore are gas dwarfs. Also called mini-Neptunes, gas dwarfs are up to four times as big as Earth and have a rocky core, unlike gas giants such as Jupiter. They are less massive than Neptune but have the same hydrogen- and helium-rich atmosphere, which have the potential to support life.
Astronomers look for biosignatures – chemical footprints that point to the presence of organisms – when hunting for aliens. But performing such searches on gas dwarfs are not easy since these worlds do not exist in our solar system. Scientists have to observe exoplanets, or worlds that orbit a star other than the sun. Unfortunately, exoplanets are too far away and existing observatories are not powerful enough to make precise observations.
But NASA’s newest telescope may just do the job. Deemed as the successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, the agency’s longtime eyepiece into the cosmos, Webb is the largest, most powerful space observatory ever built. It can peer farther back into time than Hubble is capable of doing, thanks to its much larger mirror.
For their study, Phillips and her team simulated Webb observations to examine how well the telescope detects ammonia, a potential biosignature, on seven potentially habitable gas dwarfs. The researchers incorporated various cloud conditions into planetary models to quantify how significant Webb’s detection is.
The simulation showed that Webb could detect ammonia in as little as 60 hours. After about ten orbits around the sun, the observatory would have collected enough data to determine whether aliens live on a gas dwarf.
“Humankind has contemplated the questions, ‘Are we alone? What is life? Is life elsewhere similar to us?”’ Phillips remarked. “My research suggests that for the first time, we have the scientific knowledge and technological capabilities to realistically begin to find the answers to these questions.”
A primer on James Webb Space Telescope
Webb will be launched into space in October 31, 2021. It will orbit the sun around a million miles from Earth, but will take as long as the planet to complete an orbit.
“What is special about this orbit is that it lets the telescope stay in line with the Earth as it moves around the sun,” NASA said. “This allows the satellite’s large sunshield to protect the telescope from the light and heat of the sun and Earth.”
The observatory will be mainly used for studying the history of the universe, beginning from the Big Bang to the formation of star systems that are capable of supporting life. Scientists also plan to avail of Webb to study a host of other things, including dark matter.
Richard Massey, a professor of cosmology at Durham University in the U.K., is part of a team that is working to understand what dark matter is.
“Dark matter is invisible. But in this same patch of sky, we used the Hubble Space Telescope to make the first 3D map of dark matter, by noticing how it affects all the visible things around it. Now, the JWST will zoom in on individual clumps of dark matter with unprecedented resolution.”
Cosmic.news has more about the search for alien life.
Space
Demonic face appears above surface of sun during biggest geomagnetic storm in almost 20 year
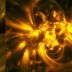
The sun appears to be angry; a massive coronal mass ejection unveils a striking image resembling a grimacing demonic face. Striking are the letters DV (DeVil?) standing out on the forehead of the figure.
Obviously, the strange phenomenon captured by NASA’s solar satellite SOLO EUI HRI 174 on 2024/05/11 is an ordinary natural occurrence triggered by the eruption of solar material but a fact is that a huge CME hit Earth’s magnetic field on May 10th, leading up to the biggest geomagnetic storm in almost 20 year.
And it is not yet over as forecasts predict additional coronal mass ejections to follow closely behind, prolonging the storm well into the weekend. Anticipation mounts for widespread auroras, promising captivating displays over regions like Europa and the United States.
The storm has now reached level G5 which is the strongest level of geomagnetic storm, on a scale from G1 to G5. The solar storm could lead to disruption of satellite communication systems, low-frequency radio navigation systems such as GPS or even widespread power grid failures.
This unique solar phenomenon emphasizes once more the importance of constant monitoring and readiness in response to solar disruptions in order to prevent another Carrington event which was the most intense geomagnetic storm in recorded history, peaking from 1–2 September 1859.
Space
GOD’S JUDGMENT WARNING? April solar eclipse to cast darkness across 7 U.S. towns named “Ninevah” from the Bible

In a recent broadcast, Mike Adams from Brighteon Broadcast News
discussed the upcoming solar eclipse set to pass through southwest Texas
on Monday, April 8th, 2024. The event is expected to draw large crowds
of people eager to witness the celestial phenomenon, with Dripping
Springs residents having a particularly great view.
As the Path of Totality extends across several states in the
United States, including Texas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Missouri, Illinois,
Indiana, Ohio, New York, Pennsylvania, Vermont, New Hampshire, and
Maine, many counties have declared emergencies ahead of the event.
Officials from Travis County, Kendall County, and Bell County are among
those issuing disaster declarations in anticipation of large crowds,
increased traffic, and significant strain on first responders,
hospitals, and roads during the days leading up to and after the
eclipse.
County officials have advised residents to stock up on food,
water, and essential supplies for at least three days, as well as
filling their vehicles with gas. Hays County Director of the Office of
Emergency Services, Mike Jones, recommended visiting stores and gas
stations in advance to reduce traffic flow and manage expectations
regarding the influx of visitors to the county.
Despite the potential for increased traffic and crowds during the
solar eclipse, it remains unclear how these factors would warrant
emergency preparations on such a large scale. Critics question whether
the recommendations to stock up on food and water are necessary or
proportionate to the event’s duration and impact.
Adams also pointed out that authorities rarely warn the public
about other potential dangers, such as financial collapse or an influx
of immigrants. They questioned why solar eclipses are considered more
threatening than these issues.
The Allais Effect that seems to alter the laws of physics during solar eclipses
Additionally, the interviewer brought up the “Allais Effect” – a
phenomenon that occurs during solar eclipses where strange occurrences
or changes in behavior may be observed. The eyewitness encouraged others
to look into this intriguing aspect of solar eclipses and not let
misplaced fears deter them from experiencing such an awe-inspiring
event.
Adams further delved into the intriguing world of the Allais
Effect, a phenomenon that occurs during eclipses and has confounded
scientists for centuries. According to multiple confirmed experiments,
the Allais Effect causes pendulums to swing in a bizarre pattern,
reversing their precession during an eclipse.
The precession of a pendulum is typically explained by
traditional science as the rotation of the Earth underneath the
pendulum, causing it to trace a large circle on the ground. However,
during an eclipse, this precession mysteriously reverses itself, defying
conventional understanding of physics.
One paper from scirp.org suggests that anisotropic dark flow
acceleration could explain the Allais Effect. This phenomenon occurs
when the moon someone alters the gravity effects of the sun, potentially
affecting the precession of pendulums.
However, other researchers disagree with this explanation and
argue that there is something else happening during eclipses. The
interviewer mentions reading papers on this topic that suggest the sun’s
gravity well aligning with the moon’s and Earth’s could create a unique
situation where gravity behaves in an unpredictable manner, affecting
the precession of pendulums.
The ally effect remains a mysterious phenomenon that scientists
have been unable to fully explain. As researchers continue to study this
enigmatic occurrence, one thing is certain: eclipses hold a unique
power over our understanding of physics and the natural world.
Could gravitational changes result in earthquakes that happen alongside solar eclipses?
This mysterious force has been observed and reproduced in various
laboratories throughout history, though its exact nature remains
unknown. Adams asked whether these changes in gravity could potentially
trigger fault lines, such as the New Madrid fault line in Missouri. If
tectonic plates are affected by shifts in gravity, it might cause
earthquakes. While Adams did not predict an imminent earthquake, he
pointed out that pendulums and other celestial bodies do exhibit strange
gravitational behavior during eclipses.
Many cultures have long feared eclipses due to their association
with earthquakes and other natural disasters. Adams suggested that this
connection could be more than just superstition, but rather a real
physical phenomenon still not understood by modern science. He
emphasized that gravity is not a force, but rather a curvature of
space-time, which might explain why we don’t feel its effects when
experiencing falling weightlessness.
In conclusion, the Allais Effect and its potential connection to
earthquakes during eclipses remains a fascinating and unexplained
phenomenon. As our understanding of gravity continues to evolve, so too
may our comprehension of these mysterious events that have captivated
humanity for centuries.
Might some government officials have knowledge of imminent events far more dangerous than an eclipse?
In the broadcast, Adams posited a theory that certain individuals
within the government may have been informed about anticipated major
disasters like earthquakes, leading to stockpiling of food, gas, water,
and other emergency supplies. This would make sense considering
hospitals would likely become overwhelmed, and high-rise buildings in
areas like Austin Travis County could collapse during such an event.
Adams stated that governments and continuity of government
operators might have received secret warnings about potential
earthquakes along the New Madrid fault line or elsewhere in the Midwest.
Was a New York National Guard helicoper shot down by drug cartels near the U.S.-Mexico border?
Continuing with the broadcast, Adams revealed concerns over the truth
behind a recent helicopter crash near the border that resulted in the
death of two New York National Guard soldiers and left another soldier
critically injured. The journalist shared insights from a source with
extensive experience as both a civilian pilot and former military pilot.
The source analyzed the crash of the UH-72A Lakota helicopter,
which struck the ground vertically or near vertically without any signs
of rotational damage. The most likely cause, according to the analysis,
is not a mechanical malfunction but rather a shoot down by an IR missile
warhead that would have taken out the engine and damaged the rotor
cyclic and collective controls, making an auto rotation impossible.
Auto rotation is a common maneuver for helicopter pilots when
they lose power, allowing them to descend safely by converting their
vertical descent into rotor speed. However, this requires sufficient
altitude, which may have been lacking in this case. The journalist’s
source believes that the most likely cause of the crash was a
ground-to-air missile or similar weapon, such as an RPG.
The journalist emphasized the importance of being prepared for
unusual events and called into question the honesty of government
officials regarding such incidents. With concerns about missing
ground-to-air missiles and potential cover-ups, it is crucial that the
public remains vigilant and demands transparency from those in power.
The State Department has expressed alarm over the potential use
of ground-to-air missiles by these criminal organizations, which could
pose a threat to commercial aircraft and US military assets in the
region.
Chased in her vehicle by human traffickers near the U.S.-Mexico border
Adams also highlights the growing danger faced by residents of border
communities, such as those in Texas, where human trafficking operations
are preying on unsuspecting individuals. One harrowing account shared
in the broadcast describes a woman being chased by drug smugglers while
driving to her family’s ranch near the border. The incident underscores
the escalating violence and lawlessness that has taken hold in these
areas, with criminal organizations becoming increasingly bold and
aggressive in their activities.
The lack of action by the US government to secure the border has
allowed narcos to continue expanding their operations and acquiring more
powerful weapons systems. This includes potentially obtaining RPGs or
other missile-like devices that could be used to shoot down military
aircraft. As these criminal organizations become better equipped, the
danger to both border communities and US military assets in the region
will only grow.
As the situation along the US-Mexico border continues to
deteriorate, it is clear that more must be done by the US government to
address this growing crisis. The safety and security of both American
citizens living near the border and US military assets in the region are
at stake as these criminal organizations become increasingly emboldened
and better equipped.
In one incident described by Adams, a concerned Texas rancher
recounted the harrowing experience they faced when a group of suspected
smugglers trespassed on their property, putting their family’s lives at
risk. The rancher described the tense situation that unfolded as the
intruders attempted to roll their car and engage in high-speed chases on
their land.
The rancher’s account of the incident highlights the growing
concern among border state residents about the escalating violence and
criminal activity associated with the ongoing immigration crisis. As
smugglers and other criminals continue to exploit the porous US-Mexico
border, families living in affected areas are left feeling vulnerable
and unsafe in their own homes.
Fortunately, the rancher’s husband was able to intervene and
block the intruders from entering their property. However, this is not
always the case for other residents who have fallen victim to similar
incidents. The rancher emphasized that it is essential for people living
near the border to be prepared to defend themselves and their families
against potential threats.
In conclusion, the ongoing immigration crisis has created a
dangerous reality for many families living along the US-Mexico border.
As smugglers and other criminal elements continue to exploit weaknesses
in border security, it is crucial for residents to be prepared to
protect themselves and their loved ones from potential harm. The
rancher’s harrowing experience serves as a sobering reminder of the very
real dangers that exist in this increasingly hostile environment.
Suspicions rise over possible 15-minute city in Maui, following the burning down of Lahaina
In an exclusive interview, concerns have been raised regarding the
potential establishment of a 15-minute city project on the island of
Maui. Adams played a video featuring an advertisement for what appears
to be a 15-minute city project on Maui. The ad showcased paid actors
promoting walkable and bikable neighborhoods designed for people to
spend time together without owning cars. However, Adams pointed out that
the actors seemed unnatural and suggested they were reading from a
teleprompter.
Further investigation into the website mentioned in the video,
housemaui.com, revealed its connection to wildfire survivors on Maui.
The site provides housing resources for those affected by the recent
fires. However, the interviewee believes this recovery effort is
actually a cover for building a 15-minute city. The Hawaii Community
Foundation is mentioned as providing financial resources to support the
recovery efforts from the wildfires on Maui. Critics argue that this
recovery may be more about constructing a 15-minute city than assisting
those impacted by the fires.
Adams raised further concerns about the rebuilding efforts in
Lahaina, Hawaii following a devastating fire. The interviewee questioned
the motives behind the proposed “15 Minute Blue City” plan, expressing
skepticism over the involvement of globalist organizations and
government entities in the rebuilding process, suggesting that the focus
should be on rebuilding homes for surviving families rather than
creating a new utopian city.
The website of one of the collaborating organizations mentions
working with government builders, financiers, cultural and environmental
groups, and residents to design policies supporting housing
affordability. This raised suspicions of a liberal “Utopian” 15-minute
city being created under the guise of affordable living.
Adams also highlighted the stark contrast between the support
provided to other countries and the lack of assistance given to Lahaina
and US veterans. While billions of dollars are allocated to Ukraine and
Israel, very little is spent on rebuilding efforts in Lahaina or
addressing the US border crisis. Adams also noted the preferential
treatment given to illegal immigrants in cities like New York and
Chicago, who receive various benefits such as free housing, phones,
insurance, legal representation, and COVID stimulus checks.
Solar eclipse to pass through seven U.S. towns named “Nineveh”
Continuing with the broadcast, Adams discussed the significance of a
solar eclipse passing through seven towns in North America named
Nineveh, drawing parallels to the biblical story of Jonah and the city
of Nineveh. The towns, all bearing the name of the ancient Assyrian
capital, have been named after the biblical city known for its
repentance and divine intervention.
Adams explained that the town of Nineveh was known for its
wickedness but was ultimately spared from destruction after its
inhabitants repented upon hearing Jonah’s message. “Jonah was
essentially sent to Nineveh to preach to the people, but he didn’t want
to go because it was such a cesspool of filth and sin,” Adams said.
The people of Nineveh ultimately heeded Jonah’s warning and
repented en masse. “Every single one of them, it says from the King down
to the lowest peasant, they all repented,” Adams stated. “Everybody
fasted. That’ll never happen in America.”
Adams also mentioned that Nineveh was eventually destroyed, but
not by God. The city’s destruction came at the hands of its longtime
enemy, Israel. “Nineveh was the capital city of Assyria, which is the
the longtime enemy of Israel,” the interviewer said. “The geolocation of
Nineveh today is in Iraq.”
The solar eclipse’s path through seven towns named Nineveh has
raised questions about whether this event could be considered a divine
coincidence or a message from God. The journalist noted that if one
believes in coincidences, it would be an interesting occurrence for the
solar eclipse to pass through these specific towns.
In conclusion, Adams highlighted the importance of understanding
the significance of events like the solar eclipse and their connections
to historical stories such as Jonah and Nineveh. “If you think about the
fact that this this solar eclipse is going through seven towns in North
America that are named Nineveh that have been named, obviously, after
this biblical town,” the interviewer said, “and what an odd coincidence
it is, if you believe in coincidences, that this would traverse the path
of crossing all seven towns.”
Adams further pointed out that the number seven holds great
significance in the Bible, often representing God’s presence or
intervention. With this eclipse passing through seven towns named Niveh,
some are wondering if it could be a sign of judgment or a call for
Americans to change their ways.
The path of the solar eclipse will travel through Central Texas,
Arkansas, Southeastern Missouri, Southern Illinois, and Southern Indiana
in the United States before crossing into Canada. While these areas are
predominantly Christian, the interviewee argues that the message may be
intended for the entire nation, as this is a national event and the
next time such an occurrence will happen in North America is in the year
2044.
Some scientists and physicists might dismiss the idea of divine
intervention in the motion of celestial bodies; however, Adams poses the
question that if God has knowledge of these motions due to His
omniscience, and He is the one who set everything in motion, then could
this not be a sign from Him?
The solar eclipse on April 8, 2024, may simply be an astronomical
event or a fascinating coincidence. However, for some, it raises
questions about whether America is being judged or warned through the
celestial alignment of the Sun, Moon, and Earth. As the nation awaits
this rare phenomenon, these discussions will continue to provoke thought
and reflection on the role of faith in understanding the world around
us.
Is America ready to repent for its sins against children and God?
Many people believe that if America does not repent for its sins and
change its ways, it will face the wrath of God in the form of natural
disasters and other catastrophes. The interviewer asked whether America
is ready to repent and reject its evil ways, such as abortion and
transgenderism. Adams expressed skepticism, stating that most Americans
are not willing to change their ways or acknowledge God’s existence. He
believes that only a small portion of the country would be prepared to
repent, while the majority remains entrenched in evil and worships Satan
instead of Jesus Christ.
When asked how one could vote in a hypothetical cosmic poll
conducted by God on whether to unleash judgment against America or not,
Adams emphasized that even those who are devout Christians and follow
the teachings of Christ would be affected if God decides to judge the
nation. The consequences of such divine intervention would be
far-reaching and devastating for all Americans, regardless of their
personal beliefs or actions.
Adams reiterated a call to reflect on the potential consequences
of America’s continued refusal to repent and turn towards God. As the
country faces increasing signs of judgment, it remains unclear whether
any significant change will occur before it is too late. This epic
cosmic battle between good and evil will inevitably lead to collateral
damage, with innocent lives being lost due to the destructive nature of
the conflict.
Adams says that while they desire for God to ultimately defeat
Satan, he recognizes that this war may result in significant harm to
those who are not directly involved in the battle between good and evil.
He explained that innocent people could be caught in the line of fire
as a result of area effect weapons or other catastrophic events
unleashed by God during the conflict.
Despite acknowledging the potential for harm to come to innocent
individuals, God’s ultimate goal is to defeat evil and restore order to
the world. Those who find themselves in the path of destruction may
still be granted entry into heaven. However, Adams warned that when God
unleashes his wrath on a nation, it is not limited to specific targets
or individuals. Instead, the entire country may be affected by the
consequences of this cosmic battle. As a result, he advised Americans to
prepare for potential disasters by preparing to shelter in bunkers, or
other safe locations away from urban areas and blast zones.
(Article by Mike Adams republished from NaturalNews.com )
-

 Ghosts2 years ago
Ghosts2 years agoZozo: The Ouija Board Demon
-

 Space2 years ago
Space2 years agoScientists claim to have found the answer what existed before the Universe
-

 Ghosts2 years ago
Ghosts2 years agoOld Coot of Mount Greylock
-
Archaeology1 year ago
New discoveries at Ekʼ Balam during conservation works
-

 General3 years ago
General3 years agoUC San Francisco engaging in horrifying experiments, organ harvesting of live babies in the name of “science”

