Archaeology
Archaeologists recover Aztec Codices of San Andrés Tetepilco
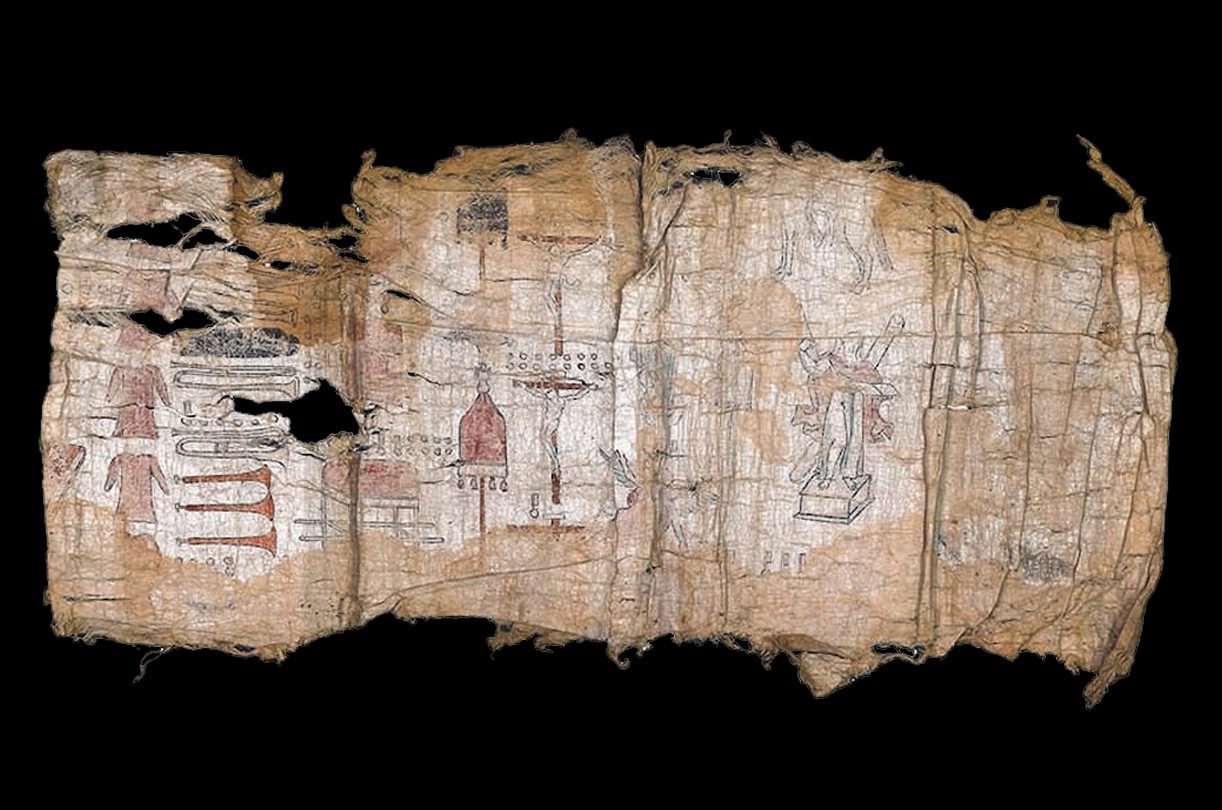
Archaeologists from the National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH) have announced the recovery of the Codices of San Andrés Tetepilco.
The three codices date from the late 16th to early 17th century and are believed to be a continuation of the Boturini Codex.
The codices depicts a transition from pre-Hispanic Mexica to the arrival of the Spanish, the latter represented with the image of Hernán Cortés who appears dressed like a Roman centurion. Another scene corresponds to the reign of Izcóatl, the fourth king of Tenochtitlan, and the founder of the Aztec Empire.
Image Credit : INAH
According to a press statement, the collection was in private ownership and has been acquired for the National Library of Anthropology and History (BNAH).
Following confirmation of authenticity by experts, INAH, in collaboration with various companies and philanthropists raised 9.5 million pesos (237,115.00 Pound sterling) for the purchase.
A closer examination has revealed that the codices were made on amate, a type of bark paper, with an applied layer of gesso and cochineal extract. Inks used to paint the various scenes come from plants, charcoal, indigo, and different shades of ochre.
Image Credit : INAH
Speaking to HeritageDaily, a representative of INAH said: “It wasn’t until two years ago that BNAH authorities were able to see them directly and manage a study to confirm their authenticity, which has involved the analysis of their composition by experts from the UNAM Physics Institute and the Coordination National Conservation of Cultural Heritage of the INAH.”
“Thanks to the transfer of ownership, the people of Mexico now hold the Codices of San Andrés Tetepilco which are part of the so-called mixed codices, as they contain paintings from indigenous tradition and texts in Nahuatl or Spanish, written with the European alphabet,” added INAH.
Header Image Credit : INAH
Sources : INAH
This content was originally published on www.heritagedaily.com – © 2023 – HeritageDaily
Archaeology
Archaeologists search for traces of the “birthplace of Texas”

As part of a $51 million project, archaeologists have conducted a search for traces of Washington-on-the-Brazos, also known as the “birthplace of Texas”.
Washington-on-the-Brazos was a small town along the Brazos River in Washington County, Texas.
The town is best known for being the site of the Convention of 1836 and the signing of the Texas Declaration of Independence from Mexico in the Texas Revolution.
The declaration officially established the Republic of Texas, however, no other government or nation recognised the newly declared nation.
The town went into decline due to poor transport links and competition from surrounding towns and cities. This resulted in Washington-on-the-Brazos being mainly abandoned by the townsfolk in the late 1800s who relocated to Brenham or Navasota.
Archaeologists have recently completed a $51 million excavation along the La Bahia Road, the main highway through the town that carried goods and travellers across the state from Goliad to Nacogdoches.
Researchers used tax records and official documents to identify where former buildings were situated, followed by geophysics to detect anomalies beneath the ground in preparation for exploratory excavations.
Image Credit : Texas Historical Commission
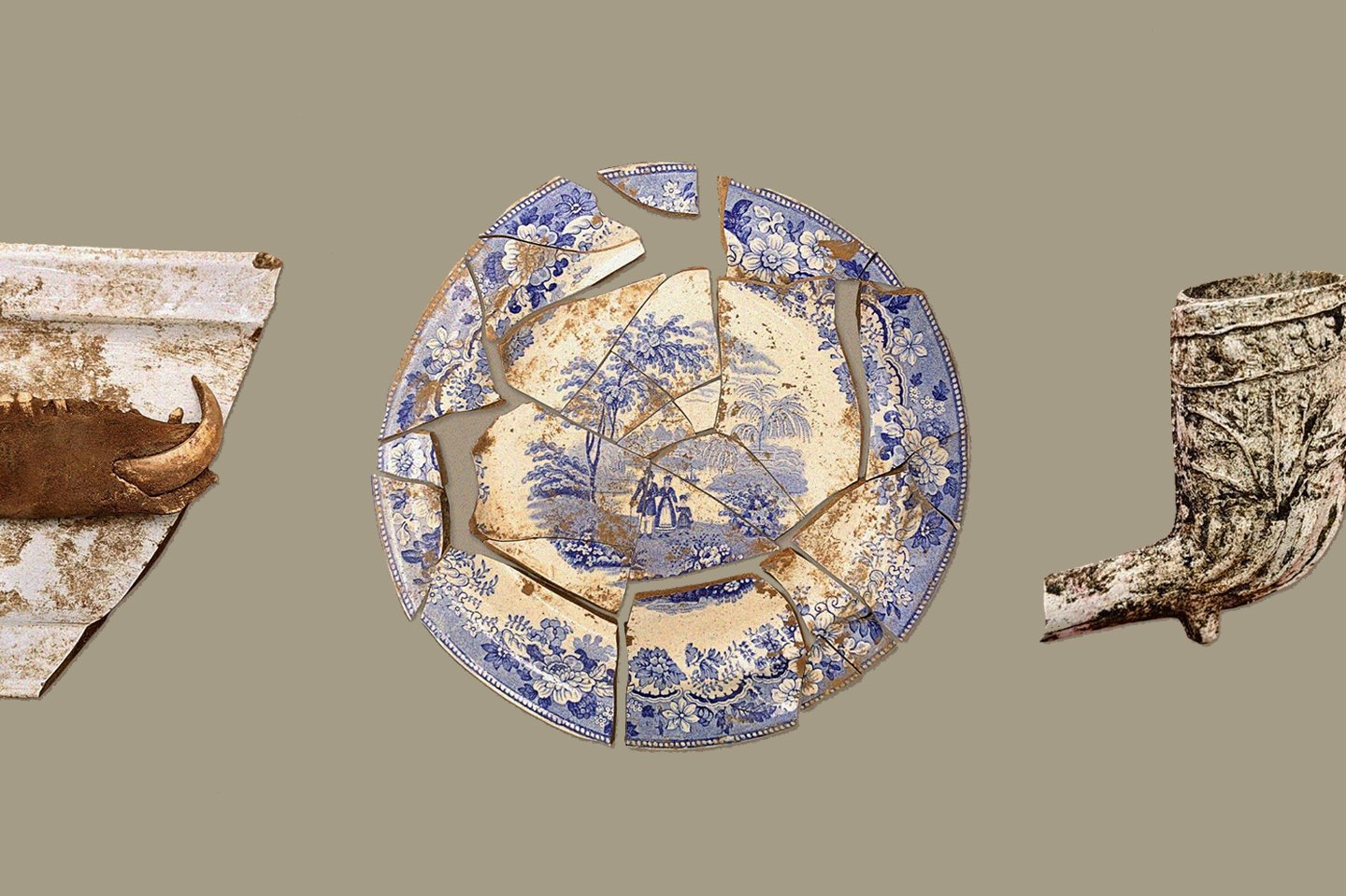
This led to the discovery of where the Houston’s presidential office once stood, revealing the footprint of a 16-by-16-foot building along with objects such as nails, buttons, ceramics, and window glass.
Archaeologists also uncovered the brick floor of a house from the 1830’s, in addition to the remains of an old brick fireplace.
Over 10,000 artefacts have been recovered during the project, which include the key to a gold pocket watch, gun flints, buttons from a soldier’s uniform, and an 1831 U.S. dime.
According to a press statement by the Texas Historical Commission (which manages the site), several buildings from the town will be faithfully (partially or fully) recreated to enable visitors to visit the buildings that once lined the La Bahia Road.
Header Image Credit : Texas Historical Commission
Sources : Texas Historical Commission
This content was originally published on www.heritagedaily.com – © 2023 – HeritageDaily
Archaeology
Archaeologists find moated medieval windmill
Archaeologists from MOLA (Museum of London Archaeology) have uncovered a moated medieval windmill during construction works of the National Highways A428 Black Cat to Caxton Gibbet improvement scheme in Bedfordshire, England.
According to the researchers, the mill dates from between 1066 to 1485 during the medieval period.
Owning a mill would have been a great position of power for the local lord of the manor. The lord received money for the flour and rent from local tenants who farmed the land around it.
Excavations have revealed that the mill had a large central post used to orient the sails towards the wind. The post was found partly buried in a large mound used for support, making it a sunken type of Post Mill that first appeared in Europe from the 1100s to 1200s.
No physical remains of the mill survives above ground and the mound it stood on was levelled for farming. However, upon removing the topsoil, archaeologists found traces of a moat ditch surrounding the structure.
A moat is not unusual for sunken type Post Mills, as the excavated soil from the ditch was used to build the mound where the larger mill structure was situated.
According to a representative from MOLA: “Because this area is naturally very wet, the deep ditch would have collected water and become a moat. We could see evidence for this during our excavations because it was full of shells from water snails!”
Cut trenches called ‘slots’ were sunk into the ditch, revealing various pottery sherds, including medieval green glazed ware, in addition to animal bones, iron nails (likely from the wooden mill building), farming tools, clay tobacco pipe stems, and 17 pieces of millstones.
Header Image Credit : MOLA
Sources : MOLA
This content was originally published on www.heritagedaily.com – © 2023 – HeritageDaily
-

 Ghosts2 years ago
Ghosts2 years agoZozo: The Ouija Board Demon
-

 Space2 years ago
Space2 years agoScientists claim to have found the answer what existed before the Universe
-

 Ghosts2 years ago
Ghosts2 years agoOld Coot of Mount Greylock
-
Archaeology1 year ago
New discoveries at Ekʼ Balam during conservation works
-

 General3 years ago
General3 years agoUC San Francisco engaging in horrifying experiments, organ harvesting of live babies in the name of “science”
