Archaeology
The Alaca Höyük meteoric dagger
The Alaca Höyük meteoric dagger is an iron forged dagger with extraterrestrial origins.
During the Bronze Age, iron was more valued than gold (evidenced in the Kültepe tablets of 1950 BC), and very few ancient cultures had the smelting technology to extract a low-quality iron from limited sources of iron–nickel alloys.
Extracting usable metal from iron ore required maintaining a temperature of 1,500 °C (2,730 °F) and an advanced understanding of metallurgy using kilns or furnaces.
Sources of Iron were limited to meteoric iron, an early-universe protoplanetary-disk remnant found in iron meteorites made from the elements – iron and nickel. Iron meteorites are mainly thought to originate from M-type (aka M-class) asteroids which are the remnant cores of early protoplanets during the early formation of our solar system.
The Hittites were one such culture that is believed to have developed iron smelting technology during the middle of the 2nd millennium BC.
The Hittites were an Anatolian people who established an Empire stretching across most of Anatolia, parts of the northern Levant and Upper Mesopotamia, centred on the capital of Hattusa near modern Boğazkale, Turkey.
Most of what we know about the Hittites comes from cuneiform text written in either Akkadian (the diplomatic language of the time) or in the various dialects of the Hittite confederation, and from diplomatic and commercial correspondence found in archives in Assyria, Babylonia, Egypt and the Middle East.
From 1935–39, archaeologists excavating the Hittite settlement of Alaca Höyük discovered 14 “Princely tombs” or “Kingly tombs”, in which they found funerary offerings consisting of gold and electrum standing cups, in addition to the Alaca Höyük bronze standards and the Alaca Höyük meteoric dagger.
The dagger features an iron blade with a golden hilt and has been dated to between 2400 to 2300 BC during the Bronze Age.
An X-ray fluorescence (XRF) study of the blade in 2012 identified that iron and nickel, with trace amounts of cobalt, were the major components of the blade, with trace amounts of Ca, Zn, As, and Sr due to iron corrosion.
The study concluded the dagger was produced using meteoric iron, which was confirmed in a 2017 geochemical analysis published in the Journal of Archaeological Science. This predates the onset of the Iron Age in Anatolia and the Caucasus by almost 1000 years, where the Iron Age began around 1300 BC.
Header Image Credit : Noumenon – CC BY-SA 3.0 DEED
Sources : Japanese Institute of Anatolian Archaeology – Preliminary Report on the Analysis of an Early Bronze Age Iron Dagger Excavated from Alaca Höyük
This content was originally published on www.heritagedaily.com – © 2023 – HeritageDaily
Archaeology
Groundbreaking study reveals new insights into chosen locations of pyramids’ sites
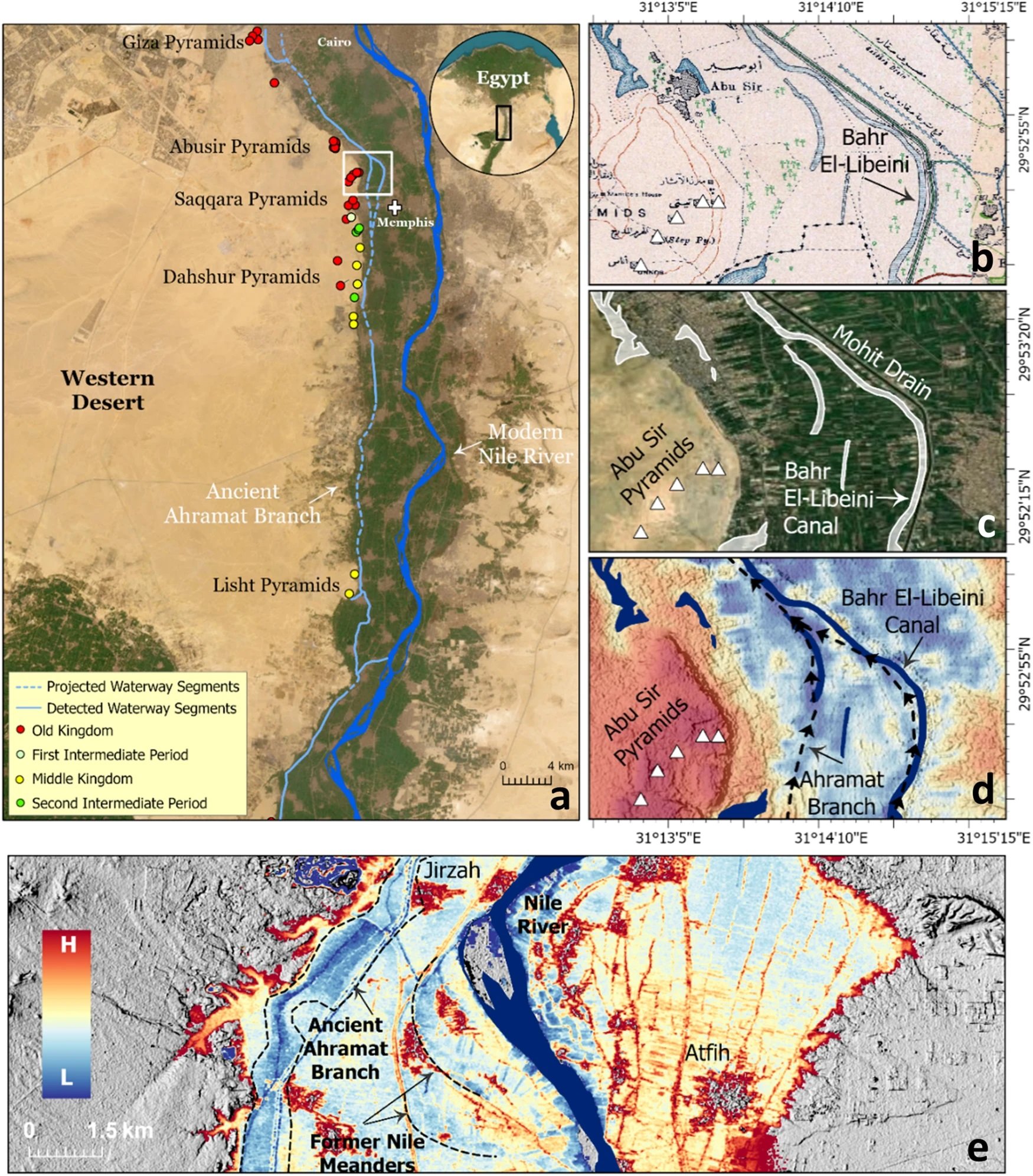
A groundbreaking study, published in the journal Communications Earth & Environment, has revealed why the largest concentration of pyramids in Egypt were built along a narrow desert strip.
Since the beginning of the Pharaonic era, the Nile River has played a fundamental role in the rapid growth and expansion of the Egyptian civilisation.
The Nile provided sustenance and functioned as the primary mode of transportation for goods and building materials, which explains why most of the main cities of the Egyptian civilisation were built in close proximity to the banks of the Nile and its peripheral branches.
Over the centuries, the primary channel of the Nile shifted laterally, causing these peripheral branches to silt up. As a result, population centres were cut off from the vital resources the river provided.
Image Credit : Eman Ghoneim et al
This is apparent with the pyramids along the Western Desert Plateau, where a majority of the pyramids are concentrated along a narrow desert strip several kilometres from the current primary channel of the Nile.
Using a combination of radar satellite imagery, geophysical data, and deep soil coring, the study has investigated the subsurface structure and sedimentology in the Nile Valley adjacent to the pyramid clusters.
This has revealed an extinct branch of the primary channel called the Ahramat Branch, which was connected to the pyramids of the Old and Middle Kingdoms via causeways and their Valley Temples.
According to the study authors: “The Ahramat Branch played a role in the monuments’ construction and was simultaneously active and used as a transportation waterway for workmen and building materials to the pyramids’ sites.”
The eastward migration and abandonment of the Ahramat Branch could be attributed to gradual movement of the river to the lower-lying adjacent floodplain or tilting of the Nile floodplain toward the northeast as a result of tectonic activity, as well as windblown sand incursion due to the branch’s proximity to the Western Desert Plateau.
Header Image Credit : Eman Ghoneim et al
Sources : Ghoneim, E., Ralph, T.J., Onstine, S. et al. The Egyptian pyramid chain was built along the now abandoned Ahramat Nile Branch. Commun Earth Environ 5, 233 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43247-024-01379-7
This content was originally published on www.heritagedaily.com – © 2023 – HeritageDaily
Archaeology
Archaeologists find Roman villa with ornate indoor plunge pool
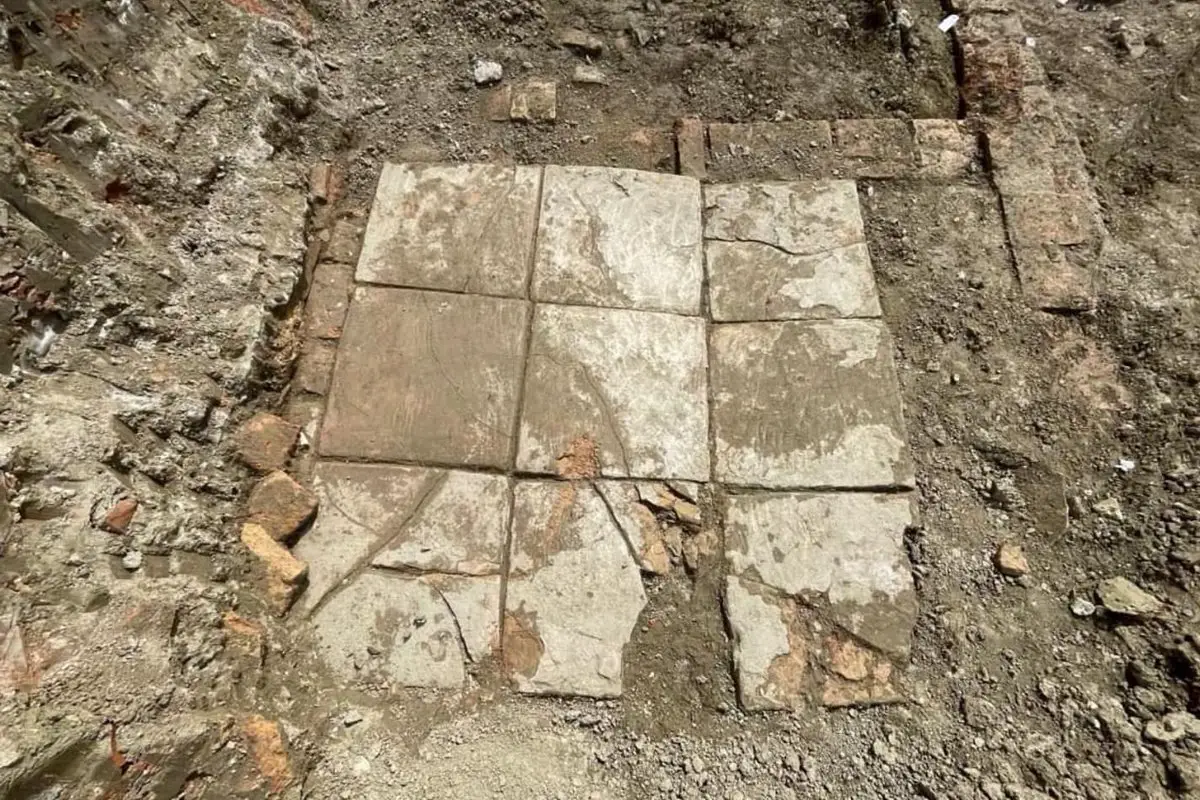

Archaeologists from the National Institute of Cultural Heritage have uncovered a Roman villa with an indoor plunge pool during excavations at the port city of Durrës, Albania.
During antiquity, Durrës was founded by Ancient Greek colonists from Corinth and Corcyra.
The colony emerged into a major trading centre, which during the Roman period was annexed into the expanding territory of the Roman Republic following the conclusion of the Illyrian Wars.
By the 4th century, the city (named Dyrrachium), emerged as the capital of the Roman province of Epirus nova, covering the region of Ancient Epirus.
Image Credit : IKTK
Archaeologists excavating a former residential part of the ancient city have uncovered a high status Roman villa that dates from between the 1st and 4th century AD.
The villa interior contains an indoor pool, richly decorated with frescoes on the walls and mosaic flooring with tiles and inlays of marble, stone, glass and ceramics. Located adjacent to the pool are shallow square basins lined with waterproof mortar, believed to be the remains of an ancient water feature.
Within the northern area of the excavation site, archaeologists found a large brick floor from a thermae, a Roman bath, and further traces of walls from the wider complex.
In the western area, the team discovered fragments of relief stucco that was used to decorate the walls and ceilings of the villa. The reliefs depict anthropomorphic and floral motifs, further indicating the wealth of the villa inhabitants.
According to the archaeologists, the villa was destroyed by an earthquake in the 4th century, corresponding with ancient sources that describe a powerful earthquake causing buildings to collapse and the city defences to crumble.
Header Image Credit : IKTK
Sources : National Institute of Cultural Heritage
This content was originally published on www.heritagedaily.com – © 2023 – HeritageDaily
-

 Ghosts2 years ago
Ghosts2 years agoZozo: The Ouija Board Demon
-

 Space2 years ago
Space2 years agoScientists claim to have found the answer what existed before the Universe
-

 Ghosts2 years ago
Ghosts2 years agoOld Coot of Mount Greylock
-
Archaeology1 year ago
New discoveries at Ekʼ Balam during conservation works
-

 General3 years ago
General3 years agoUC San Francisco engaging in horrifying experiments, organ harvesting of live babies in the name of “science”
